Culture and Organization
Working with organizational culture can be difficult to navigate, with unknown forces and factors influencing employees’ perceptions of signals and communication from the organization. The I-Trust Culture Index puts words and numbers to six key areas, supporting the change management in areas such as digital transformation.
The culture of the organisation is important for risk management, as risk culture and safety culture is essential for the behaviour of employees in relation to policies and guidelines.
The culture index covers the culture of processes, policies and guidelines as well as the organization’s compliance with legislation on personal data (EU GDPR), Anti-Money Laundering (AML), Risk Trading, etc.
Cultural Index
The Culture Index contains six main areas focusing on the organisation’s security gaps and vulnerabilities.
Behavior
Employees' and managers' understanding of the organization's goals, policies and values.
Competence
Knowledge and experience in correct use and compliance with organization policies.
Manager
Managers' ability to communicate organizational goals and policies.
Governance
Visibility of company culture.
Incidents
Employees' accept of and willingness to report incidents and breaches.
Security of processes
Index of the potential risk of company guidelines being breached.
Measurement of employee behavior with Risk Culture
I-Trust has it’s own Risk Culture methodology for culture assessment that covers awareness, understanding and compliance. Risk Culture is an analytical tool that helps to measure and create an understanding of the organization’s ability to comply with good security practice policies and guidelines – the organization’s security and risk culture.
Compliance with security policies and attitude formation is supported by addressing the culture and behaviour of the employees.
The purpose of the Risk Culture is to show whether managers and employees have received, understood and will work according to applicable policies and guidelines.
Risk Culture
The Risk Culture method is based on the individual employee’s awareness and knowledge of policies and company guidelines. That the employees understand the importance and necessity of those policies and guidelines and that they have the necessary competences to comply with them. Embedded in the practical application of Risk Culture are methods from sociology, psychology, benchmark analysis and statistical analysis.
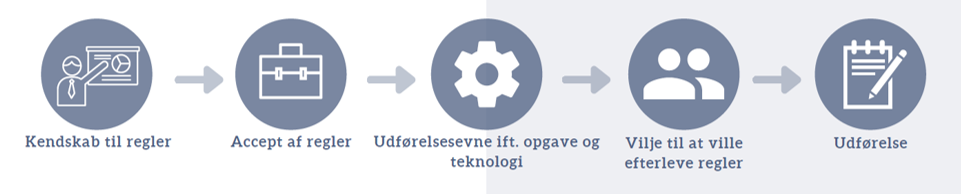
Change model in Risk Culture
Benefits for the company
- The organisation, including management, will have direct access to targeted information on the safety assessment and development of the entire organisation.
- Gap analysis of vulnerabilities and daily practice, in terms of the introduction of standards and compliance with legal requirements.
- Access to benchmark data and history
- The possibility to follow the progress of the effort through repeated safety measurements.
- A centralized tool that is easy to use and reporting that is easy to understand.

Target audiences
- Board / top management: insight into data for adjusting organizational values and behaviour
- Management (middle): insight into departmental performance (benchmark and history)
- Employees: insight into own results anonymously compared with colleagues

Themes of the study
Examination of the work on policies and guidelines:
- organisation in terms of work processes
- communication to employees
- organisation in terms of roles and responsibilities

Parts of the study
- Questions to the respondent about the work on policies in the organisation.
- Questions about guidelines for individual work processes
The I-Trust Risk Culture method has been developed and adjusted in collaboration with psychologists from Danish and German universities and tested through a large number of pilot projects in different types of companies. Today, the method is used in companies as well as in assessments of the safety culture of private citizens. Psychological theory and organizational theory, as well as experience from traffic research and safety culture in contexts other than IT, have been used to define the methodology. The practical application of Risk Culture incorporates methods from benchmark analysis, statistical analysis, etc.

